Nationwide, the average rent price fell by -0.8% to $1,720 in October, marking their 15th consecutive month of year-over-year declines and falling the most for smaller-sized units, according to Realtor.com’s October Rental Report. Realtor.com notes that new rental properties coming onto the market are expected to put continued downward pressure on rents next year.
“New multifamily construction projects started in the last two years have hit the market in 2024, with a greater supply of units helping to soften rents and bring renters some relief,” said Danielle Hale, Chief Economist at Realtor.com. “While we expect fewer multifamily homes to be finished in 2025, we still anticipate enough to increase supply, which will keep downward pressure on rents.”
For the analysis, Realtor.com examined rental data as of October 2024 for studio, one-bedroom, or two-bedroom units advertised as for-rent on Realtor.com. Rental units include apartments, as well as private rentals (condos, townhomes, single-family homes). We use rental sources that reliably report data each month within the top 50 largest metropolitan areas. Realtor.com began publishing regular monthly rental trends reports in October 2020 with data history stretching back to March 2019.
Construction boosts supply
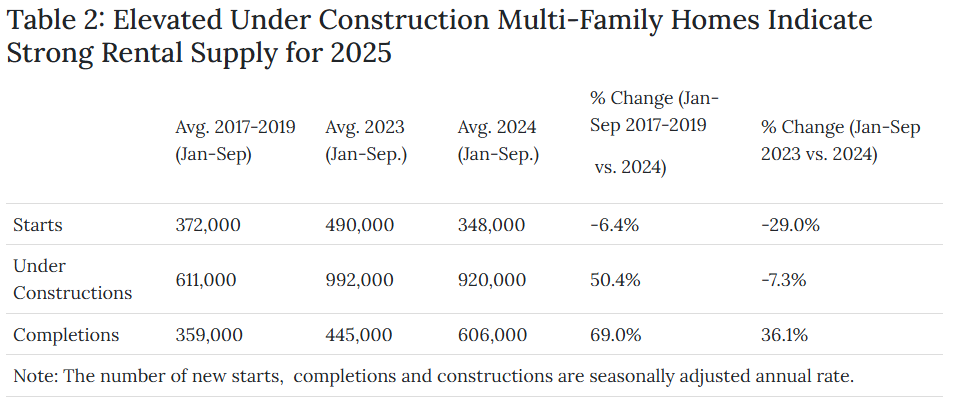
More completed multi-family homes made their way to the market in 2024, as projects started in 2022 and 2023 were completed. Between January and September 2024, the average seasonally adjusted annual rate of multi-family completions reached 606,000 units, up from 445,000 units in the same period in 2023, and higher than the 2017-19 pre-pandemic average of 359,000 units. While a lower rate of completions is anticipated for next year, rental housing stock is still expected to rise by 1.1% to more than 49 million units by fall 2025, which would be 6.7% higher than in the fall of 2019, before the pandemic.
A regional analysis
New multifamily completions rose in all regions of the country this year, with the biggest year-over-year gains seen in the South (49.1%) followed by the Midwest (44.9%), West (23.9%) and Northeast (7.4%). That has translated to lower median asking rents. In the South, the biggest annual drops in median asking rent in October were seen in Memphis, Tenn. (-5.4%), and Nashville, Tenn. (-5.2%). In the Midwest, the biggest annual decline was in Chicago (-4.1%) and in the West, rent declines were led by Denver (-5.6%) and Phoenix (-4.5%). Large Northeastern metro areas, such as New York (0.4%), have seen small increases in rent due to relatively slower increases in the supply of new rental homes.
By fall 2025 rental stock is estimated to increase most in the South, with a 1.5% year-over-year increase, followed by the West (1.2%), Midwest (0.9%) and Northeast (0.7%). That will translate to increases in the overall rental stock by 8.9% in the South, 8.6% in the West, 5.0% in the Northeast and 1.7% in the Midwest compared to pre-pandemic levels.
Rents decline across all unit sizes
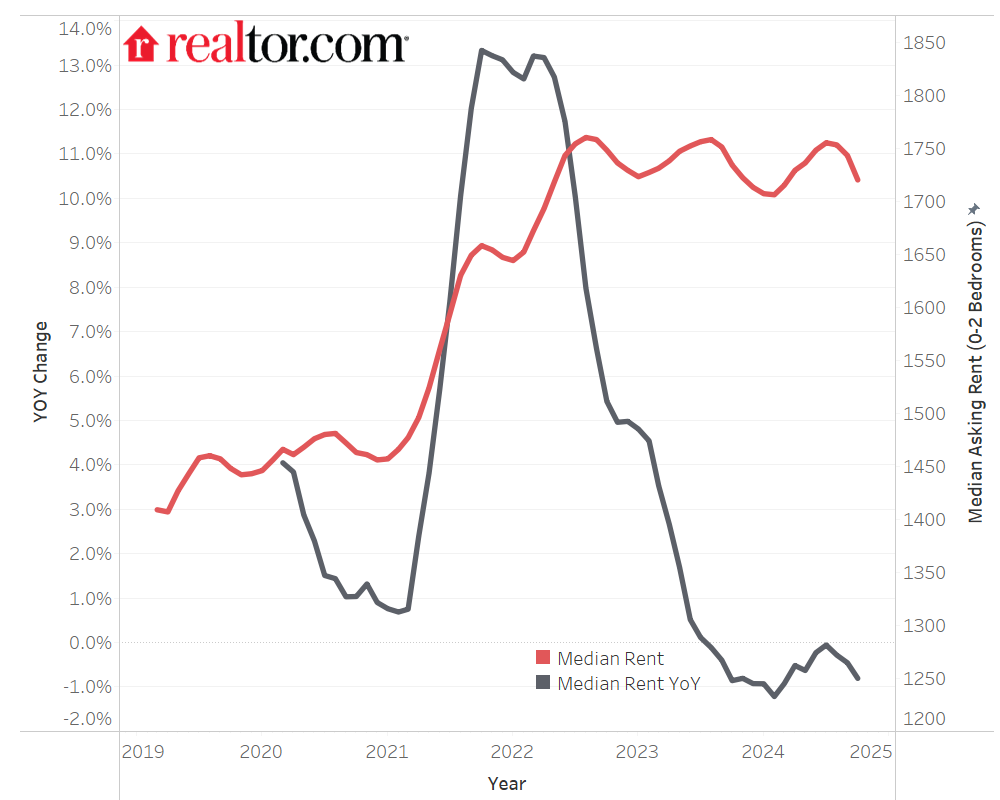
October saw the 15th straight month of year-over-year rent declines for 0-2 bedroom properties. The median asking rent fell by $14, or -0.8%, to $1,720. That’s still just $40 (-2.3%) lower than its August 2022 peak, and is $272 (18.8%) higher than the same time period in 2019.
All unit sizes saw rent declines in October, with the biggest drops in smaller-sized units. The median rent for studios fell -1.2% year-over-year, to $1,436. That’s down -3.6% from its October 2022 peak but is 12.5% higher than five years ago. The median rent for one-bedroom units fell -0.9% to $1,600, 17.1% higher than five years ago. And the median rent for two-bedroom units fell -0.7% to $1,908, which is 21.1% higher than five years ago.





