A recent analysis of Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) data by the Urban Institute dispels the myth that manufactured homes do not appreciate as much as site-built homes.
The report, which includes government-sponsored enterprise (GSE) mortgage data for manufactured homes, reveals that between 2000 and 2024, manufactured homes appreciated at nearly identical rates to site-built homes, growing approximately 5% annually. Over this period, site-built homes appreciated 212.6%, while manufactured homes followed closely at 211.8%. This data underscores the financial viability of manufactured housing, which has historically faced negative perceptions and restrictive zoning laws.
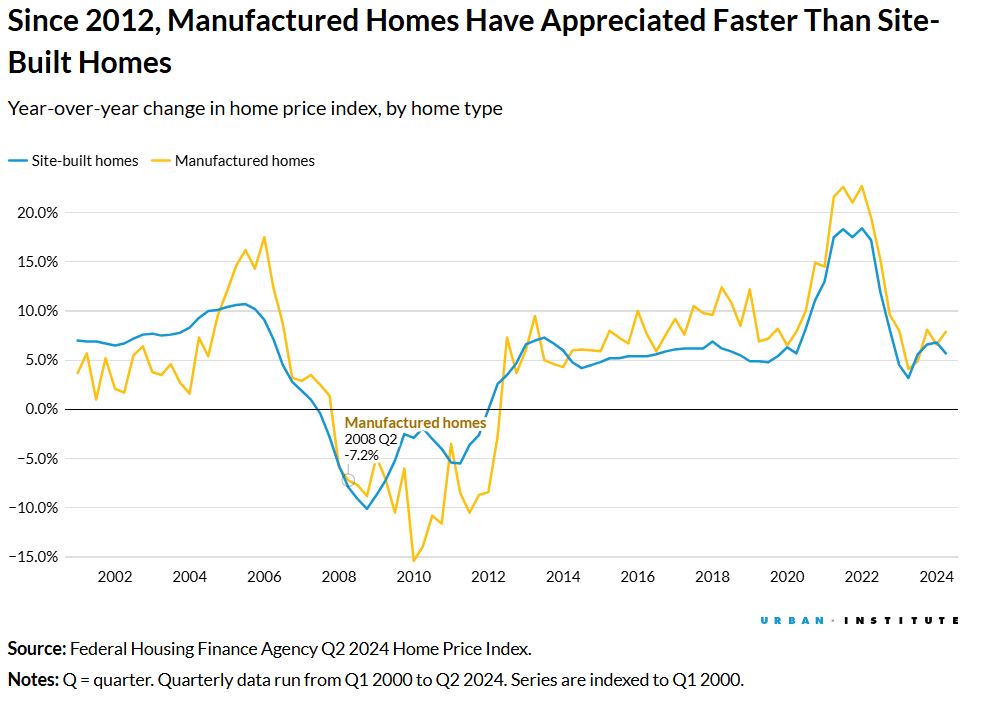
The FHFA’s methodology focuses on a repeat sale approach, analyzing price changes across multiple transactions. While the study excluded refinancing data due to lower refinancing activity in manufactured housing, it relied on purchasing indexes to provide a market-reflective valuation. Year-over-year price index data further highlighted that since 2014, manufactured homes have consistently appreciated at higher rates than site-built homes in all but two quarters.
Data Indicates Regional Trends and Limitations
The report acknowledges the role of geographic distribution in manufactured housing trends. States with high concentrations of manufactured housing, such as Texas, Florida, and North Carolina, have also experienced above-average home price growth in recent years. Between 2000 and 2024, home prices in Florida surged by 331.9%, while Texas and North Carolina recorded increases of 232.8% and 209.6%, respectively. These states accounted for 32.2% of all manufactured housing shipments in 2024 through July, potentially amplifying the overall appreciation rate for this housing category.
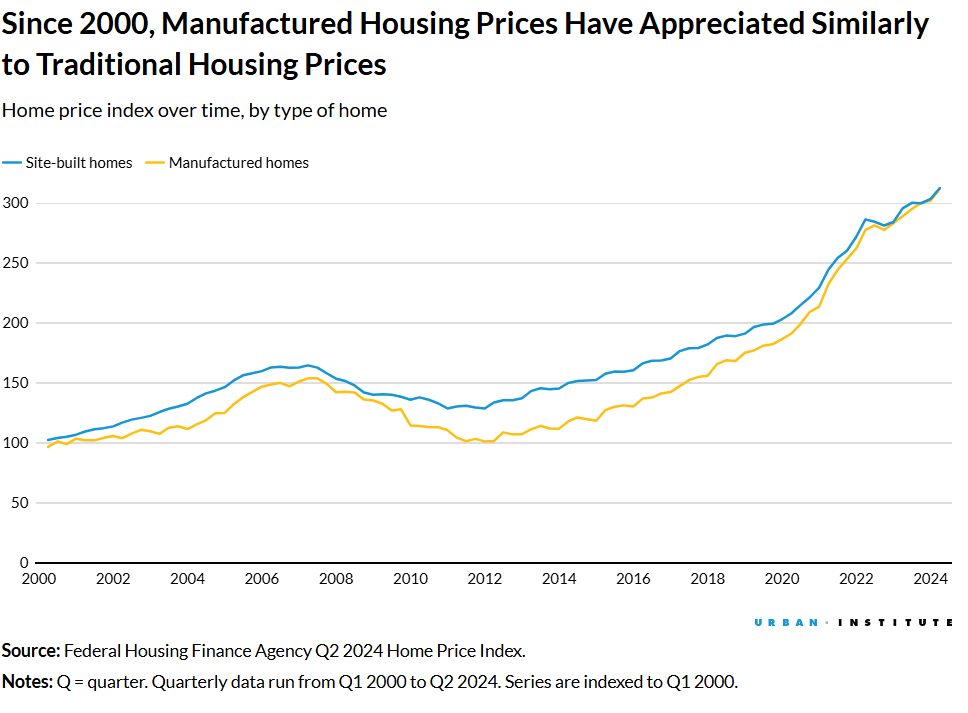
Despite the strong performance of manufactured homes on land owned by the borrower, the analysis notes a stark contrast for homes located on rented land. Research indicates that rising land prices have significantly outpaced the appreciation of home structures, contributing to a disparity in overall value growth. Land costs now comprise a larger share of home values, increasing from 35.7% in 2012 to 57.4% in 2023, according to American Enterprise Institute data.
Implications for Affordable Housing Policy
Manufactured housing presents a viable solution to the nation’s affordable housing crisis. The analysis highlights how outdated zoning laws and negative stereotypes continue to hinder the potential of manufactured homes as an affordable option. Legislative changes in states like California, Maine, and Maryland, which now permit manufactured housing in single-family zones, offer a blueprint for expanding affordable housing options. Similarly, increased federal participation in the manufactured housing market could improve mortgage standardization, reduce rates, and enhance affordability.
By highlighting the financial benefits and appreciation potential of manufactured housing, this study calls for a reexamination of restrictive policies that limit its adoption. Addressing these barriers could unlock new opportunities for affordable, sustainable housing nationwide.
Click here to view the full analysis by the Urban Institute.






